An electrocatalytic route for transformation of biomass-derived furfural into 5-hydroxy-2(5H)-furanone†
Abstract
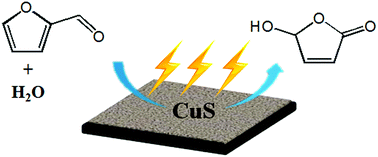
Development of efficient strategies for biomass valorization is a highly attractive topic. Herein, we conducted the first work on electrocatalytic oxidation of renewable furfural to produce the key bioactive intermediate 5-hydroxy-2(5H)-furanone (HFO). It was demonstrated that using H2O as the oxygen source and metal chalcogenides (CuS, ZnS, PbS, etc.) as electrocatalysts, the reaction could proceed efficiently, and the CuS nanosheets prepared in this work showed the best performance and provided high HFO selectivity (83.6%) and high conversion (70.2%) of furfural. In addition, the CuS electrocatalyst showed long-term stability. Mechanism investigation showed that furfural was oxidized to HFO via multistep reactions, including C–C cleavage, subsequent ring opening and oxidation, and intramolecular isomerization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...