Measuring human carboxylesterase 2 activity in pancreatic cancer patient-derived xenografts using a ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor†
Abstract
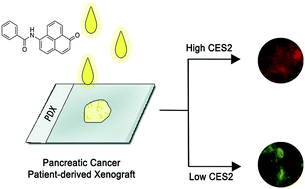
Irinotecan-based therapy is a common treatment for pancreatic cancer. To elicit its anticancer activity, the drug requires first the hydrolysis action of the enzyme human carboxylesterase 2 (hCES2). It has been established that pancreatic cancer patients have various levels of hCES2, whereby patients having low levels respond poorer to Irinotecan than patients with higher levels, suggesting that hCES2 can be used to predict response. However, current methods that measure hCES2 activity are inaccurate, complex or lengthy, thus being incompatible for use in a clinical setting. Here, we developed a small molecule ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor that accurately measures hCES2 activity in a single-step within complex mixtures. Our chemosensor is highly selective for hCES2 over hCES1, cell permeable and can measure hCES2 activity in pancreatic cancer patient-derived xenografts. Given the simplicity, accuracy and tissue compatibility of our assay, we anticipate our chemosensor can be used to predict patient response to Irinotecan-based therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...