Azabicyclic vinyl sulfones for residue-specific dual protein labelling†
Abstract
We have developed [2.2.1]azabicyclic vinyl sulfone reagents that simultaneously enable cysteine-selective protein modification and introduce a handle for further bioorthogonal ligation. The reaction is fast and selective for cysteine relative to other amino acids that have nucleophilic side-chains, and the formed products are stable in human plasma and are moderately resistant to retro Diels–Alder degradation reactions. A model biotinylated [2.2.1]azabicyclic vinyl sulfone reagent was shown to efficiently label two cysteine-tagged proteins, ubiquitin and C2Am, under mild conditions (1–5 equiv. of reagent in NaPi pH 7.0, room temperature, 30 min). The resulting thioether-linked conjugates were stable and retained the native activity of the proteins. Finally, the dienophile present in the azabicyclic moiety on a functionalised C2Am protein could be fluorescently labelled through an inverse electron demand Diels–Alder reaction in cells to allow selective apoptosis imaging. The combined advantages of directness, site-specificity and easy preparation mean [2.2.1]azabicyclic vinyl sulfones can be used for residue-specific dual protein labelling/construction strategies with minimal perturbation of native function based simply on the attachment of an [2.2.1]azabicyclic moiety to cysteine.
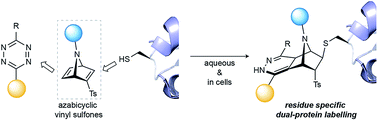


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...