The opposite and amplifying effect of B ← N coordination on photophysical properties of regioisomers with an unsymmetrical backbone†
Abstract
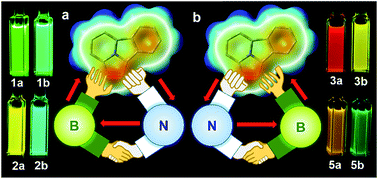
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition of pyrido[2,1-a]isoindole with internal alkynes functionalized by a BMes2ph and an N-aromatic heterocycle leads to the formation of two types of regioisomers (major a and minor b) that have distinct physical and photophysical properties. Examination on 5 pairs of regioisomers unveils that the major isomers consistently have a smaller optical energy gap and emission energy than the corresponding minor isomers, which is greatly amplified by the formation of an internal B ← N bond. The regioisomers with a B ← N bond display contrasting temperature-dependent structural dynamics and response to fluoride ions, owing to an entropy-driven or fluoride initiated B ← N bond rupture/ring-opening process and the different B ← N bond strength. The opposite inductive effect and the Lewis pair properties of the dichotomic substituent units are responsible for the contrasting properties of the regioisomers in this system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...