Polymerase-amplified release of ATP (POLARA) for detecting single nucleotide variants in RNA and DNA†
Abstract
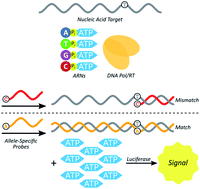
The identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) is increasingly important for diagnosis and treatment of disease. Here we studied the potential use of ATP-releasing nucleotides (ARNs) for identifying SNPs in DNA and RNA targets. Synthesized as derivatives of the four canonical deoxynucleotides, ARNs can be used in the place of deoxynucleoside triphosphates to elongate a primer hybridized to a nucleic acid template, with the leaving group being ATP rather than pyrophosphate. The released ATP is then harnessed in conjunction with luciferase to generate chemiluminescence. Extension on a long target DNA or RNA generates many equivalents of ATP per target strand, providing isothermal amplification of signal. In principle, allele-specific primers could be used in conjunction with ARNs to generate differential luminescence signals with respect to distinct genetic polymorphisms. To test this, varied primer designs, modifications, enzymes and conditions were tested, resulting in an optimized strategy that discriminates between differing nucleic acid templates with single nucleotide resolution. This strategy was then applied to diagnostically relevant alleles resulting in discrimination between known polymorphisms. SNP detection was successfully performed on transcribed mRNA fragments from four different alleles derived from JAK2, BCR-ABL1, BRAF, and HBB. To investigate background interference, wild-type and mutant transcripts of these four alleles were tested and found to be easily distinguishable amid total cellular RNA isolated from human blood. Thus, ARNs have been employed with specialized allele-specific primers to detect diagnostically important SNPs in a novel method that is sensitive, rapid, and isothermal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...