Experimental carbonation of CaO in an entrained flow reactor
Abstract
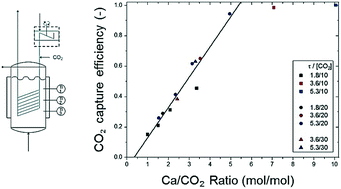
In this work, the feasibility of an entrained flow reactor for full decarbonisation of gas streams has been proved. Three CaO-based materials (two types of lime and calcined raw meal) with different textural properties and therefore, different CO2 carrying capacities have been fed to the entrained flow reactor in a series of tests in which the Ca/CO2 molar ratio and solid residence time were the operation variables studied. Up to 11 mol CO2 m−2 s−1 has been captured from the gas phase with CaO from calcined lime with a maximum CO2 carrying capacity of 0.57 mol CO2 per mol CaO, reaching CO2 capture efficiencies over 90% for a Ca/CO2 molar ratio of 5 and solid residence times under 5 s.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...