Conversion of saline waste-water and gaseous carbon dioxide to (bi)carbonate salts, hydrochloric acid and desalinated water for on-site industrial utilization
Abstract
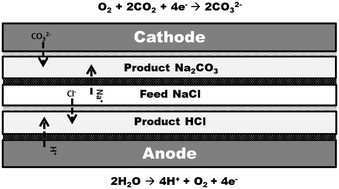
A method for the conversion of gaseous carbon dioxide and saline waste-water to desalinated water and value-added products using a new approach to electrodialysis is demonstrated and characterized. The method consists of a 5-compartment electrochemical cell including an anode, cathode and three electrodialytic compartments. Water and gaseous CO2/O2 are electrochemically converted to oxygen/protons and bi(carbonate)/hydroxide at the anode and cathode, respectively. The three central electrodialysis compartments combine the ions present in the saline water with the products of the anode and cathode to produce value-added chemicals and desalinated water. A custom-built electrochemical cell with an active area of 3.24 cm2 containing an array of two anion and cation exchange membranes each, Pt/C catalyzed cathode and titanium anode electrodes were used. The feed to the anode, cathode and central compartment were 0.1 M H2SO4, various mixtures of carbon dioxide and oxygen, and a 1 M sodium chloride stream, respectively. Clear production of hydrochloric acid, desalinated water and bi(carbonate)/hydroxide salts was observed in the respective compartments over a 24 hour period of testing. Current efficiencies of alkaline (bicarbonate, carbonate or hydroxide) ions and proton productions were as high as 71% and 96%, respectively. Polarization losses across the different compartments of the electrochemical cell were mapped to determine the source of overpotentials with different gas compositions. This concept is currently being demonstrated in a 0.5 m2 commercial scale pilot reactor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...