MoS2/carbon composites prepared by ball-milling and pyrolysis for the high-rate and stable anode of lithium ion capacitors†
Abstract
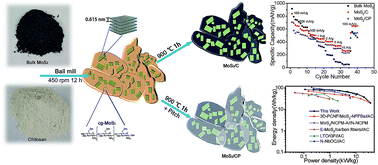
Lithium ion capacitors (LICs), bridging the advantages of batteries and electrochemical capacitors, are regarded as one of the most promising energy storage devices. Nevertheless, it is always limited by the anodes that accompany with low capacity and poor rate performance. Here, we develop a versatile and scalable method including ball-milling and pyrolysis to synthesize exfoliated MoS2 supported by N-doped carbon matrix derived from chitosan, which is encapsulated by pitch-derived carbon shells (MoS2/CP). Because the carbon matrix with high nitrogen content can improve the electron conductivity, the robust carbon shells can suppress the volume expansion during cycles, and the sufficient exfoliation of lamellar MoS2 can reduce the ions transfer paths, the MoS2/CP electrode delivers high specific capacity (530 mA h g−1 at 100 mA g−1), remarkable rate capability (230 mA h g−1 at 10 A g−1) and superior cycle performance (73% retention after 250 cycles). Thereby, the LICs, composed of MoS2/CP as the anode and commercial activated carbon (21 KS) as the cathode, exhibit high power density of 35.81 kW kg−1 at 19.86 W h kg−1 and high energy density of 87.74 W h kg−1 at 0.253 kW kg−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...