Adsorption–desorption behavior of carbendazim by sewage sludge-derived biochar and its possible mechanism†
Abstract
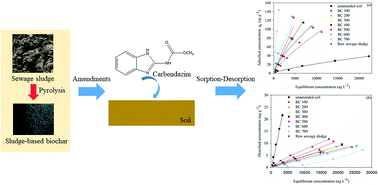
Biochar application in agricultural soil for environmental remediation has received increasing attention, however, few studies are focused on sewage sludge based biochar. The present study evaluated the effect of raw sewage sludge and sewage sludge based biochars produced at different pyrolysis temperatures (100–700 °C) on the adsorption–desorption of carbendazim in soil. Sewage sludge derived biochar significantly enhanced the sorption affinity and limited the desorption capacity of the soil for carbendazim. A maximum removal efficiency of 98.9% and a greatest value of 144.05 ± 0.32 μg g−1 sorption capacity occurred in soil amended with biochar pyrolyzed at 700 °C (BC700). As the pyrolysis temperature and the amendment rate of biochars increased, the sorption of carbendazim was promoted and desorption was further inhibited. The adsorption–desorption hysteresis index of carbendazim was consistently higher in soils amended with biochars (>0.85) than in the unamended soil (0.42–0.68), implying that carbendazim could be immobilized in soil amended with sewage sludge derived biochars. The partition effect was dominant in the sorption process for carbendazim in the biochar–soil mixtures. This study will be helpful for the disposal of sewage sludge and its utilization, and it is the first report for the study the sorption–desorption process of carbendazim in soil amended with sewage sludge derived biochar. Furthermore, these findings may be also useful for understanding the distribution and transport of carbendazim in the environment and will be of great significance in remediation strategies for contaminated soil.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...