The hydroxy-analogue of selenomethionine alleviated lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses is associated with recover expression of several selenoprotein encoding genes in the spleens of Kunming mice†
Abstract
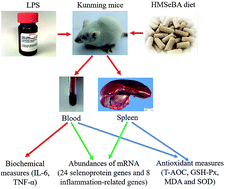
This study aimed to determine whether hydroxy-analogue of selenomethionine (HMSeBA) supplementation could alleviate LPS-induced immunological stress in mice. A total of 90 Kunming mice were randomly assigned into 5 groups. The CON-LPS and CON+LPS groups were fed basal diet (BD), the others were fed BD with different levels of HMSeBA (0.15, 0.30 and 0.45 mg Se per kg) for 4 weeks. Mice were injected with LPS (3 mg per kg BW) or the corresponding physiological saline at 14 d and 28 d. Plasma and spleens were collected at 28 d. The results showed that: (1) LPS injection decreased ADG of mice at the 3rd week, and increased the concentration of IL-6 and TNF-α in plasma and the spleen index; (2) LPS injection induced immunological stress, up-regulated 8 inflammation-related genes and 3 selenoprotein encoding genes, and down-regulated 16 selenoprotein encoding genes in spleens; (3) compared with the CON+LPS group, HMSeBA supplementation increased ADG of mice at 3 weeks and GSH-Px activity in plasma and spleens, decreased spleen index and plasma IL-6 and TNF-α levels, down-regulated mRNA levels of COX-2, ICAM-1, TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1, and up-regulated IL-10 and iNOS in spleens. 0.30 mg Se per kg of HMSeBA exhibited the optimal protective effect; (4) HMSeBA supplementation modestly recovered the expression of 8 selenoprotein encoding genes in the spleens of the stressed mice. The results indicated that HMSeBA supplementation alleviated LPS-induced immunological stress accompanied up-regulation of a subset of selenoprotein encoding genes in spleens of mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...