A mitochondria-targeted delivery system of doxorubicin and evodiamine for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer†
Abstract
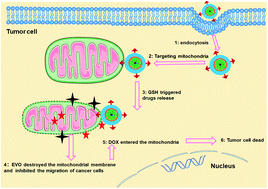
For mitochondria-targeted nano-drug delivery systems against cancer, effectively targeting and releasing the drug into mitochondria are the keys to improve the therapeutic effect. In this study, mitochondria-targeted and reduction-sensitive micelles were developed to co-deliver doxorubicin (DOX) and evodiamine (EVO) for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. After entering cancer cells, the micelles first targeted mitochondria through triphenylphosphonium cations. Then, the disulfide bonds of the micelles were cleaved by GSH, and both DOX and EVO were released near the mitochondria. The released EVO subsequently destroyed the mitochondrial membrane, resulting in a large amount of DOX entering the mitochondria and improving the anti-tumor effect of DOX. These mitochondria-targeted and reduction-sensitive micelles loaded with doxorubicin and evodiamine showed significant inhibition of the tumor cell growth both in vitro and in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...