In silico study on identification of novel MALT1 allosteric inhibitors†
Abstract
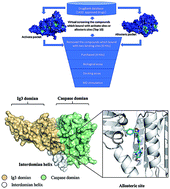
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT1), which plays a crucial role in the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation signaling pathway as a paracaspase, is a new target for immunomodulatory and antitumor drugs. Here, novel inhibitors that target MALT1 allosteric sites were identified by virtual screening FDA-approved drug databases. Paliperidone, a compound that binds to the allosteric site of MALT1, is investigated. An in vitro study found that the proteolytic activity of MALT1 substrate cleavage was blocked by paliperidone. Meanwhile, the MALT1 proteolytic activity was reversible, as demonstrated by the partial recovery of the MALT1 substrate cleavage following compound wash out. The docking analysis of the interaction of MALT1 and paliperidone suggested that two hydrogen bonds formed in the allosteric pocket of MALT1. MALT1 and paliperidone achieved a good equilibrium, as demonstrated by 100 ns molecular dynamic (MD) simulations conducted with the program Gromacs. However, the catalytically active site of the MALT1 complex with paliperidone remained in an inactive conformation. Thus, paliperidone, a noncompetitive and allosteric inhibitor, was screened through in silico and in vitro methods. This study will be of significance for the development of effective and selective drugs that can treat MALT1-driven cancer or autoimmune diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...