5-Acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin inhibits tumor cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis†
Abstract
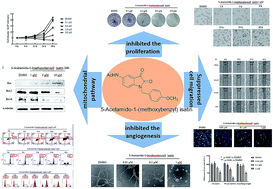
Indole and its derivatives are widely distributed in both animals and plants. Among its array of biological activities, the anti-tumor activity of indole has garnered much attention. Furthermore, the synthesis and activity of indole derivatives, including isatin, constitute a flourishing research topic. Previously, many isatin derivatives were synthesized by our group, and 5-acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin was screened as a candidate anti-tumor agent. In this study, we found that 5-acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin inhibited the proliferation of several tumor cell lines, especially the human leukemia cell line K562. Morphological observation suggested that 5-acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin induced apoptosis and caused cell cycle arrest in K562 cells. Flow cytometry revealed that 5-acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin induced mitochondrial pathway-mediated apoptosis in K562 cells. Moreover, it downregulated Cyclin B and CDC25C and upregulated p-CDC25C and p-CDK1 (Thr14), and induced K562 cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase. Findings from wound healing as well as transwell assay determined that 5-acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin could suppress migration and chemotaxis in HepG2 liver cancer cells. 5-Acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin also inhibited angiogenesis of the human umbilical vein endothelial cell line HUVEC, determined via a cell tube formation study. A clone formation study indicated that 5-acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin can inhibit tumor cell proliferation and population dependence in a concentration-dependent manner. Thus, our findings support that 5-acetamido-1-(methoxybenzyl) isatin could be used as a potential antitumor candidate in future investigations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...