Sustainable competitive adsorption of methylene blue and acid red 88 from synthetic wastewater using NiO and/or MgO silicate based nanosorbcats: experimental and computational modeling studies †
Abstract
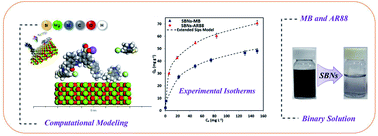
The competitive adsorption of cationic and anionic model molecules; methylene blue (MB) and acid red 88 (AR88), respectively, in aqueous solutions onto NiO and/or MgO SBNs was studied. Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and pH effect were investigated in batch modes. Computational modeling was conducted on Acclerys Material Studio for MB and AR88 adsorption. pH study showed that the adsorption is strongly pH dependent, increases for MB while decreases for AR88 with increasing the pH from 4 to 11. Isotherm studies revealed that the Sips model was the best fit for both molecules in single cases, and thus the Extended-Sips model for the binary systems. The kinetics for the binary systems were well-described by the external mass transfer model; thus, film diffusion is the most dominant in the adsorption of both organic onto the SBNs. The adsorption uptakes in binary systems exceed 130 mg g−1 for AR88 (167.7 MgO-SBNs, 132.93 NiO-SBNs, and 178.5 mg g−1 NiO-MgO-SBN), while it reached an uptake of 76.2 MgO-SBNs, 81.5 NiO-SBNs, and 94.7 mg g−1 NiO-MgO-SBNs for MB within the time needed to reach equilibrium (10 min). The adsorption of these two molecules in binary systems showed a synergistic effect onto the three types of SBNs, that enhanced the adsorption uptakes. Computational modeling confirmed the synergistic effect, the adsorption energy of binary systems was lower than that in single systems. Regeneration study was conducted over four adsorption cycles to confirm the sustainability of SBNs. They were stable under thermal oxidation at 400 °C, without any impact on the adsorption capacity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...