An amphiphilic-ligand-modified gold nanoflower probe for enhancing the stability of lateral flow immunoassays in dried distillers grains†
Abstract
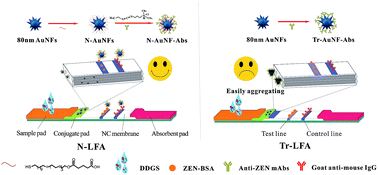
An amphiphilic ligand-capped gold nanoflower (AuNF) was proposed as a novel lateral flow immunoassay (LFA) reporter for zearalenone (ZEN) detection in distillers dried grains solubles (DDGS). The amphiphilic ligand consists of a thiol-terminated hydrophobic alkane chain, a tetra (ethylene glycol) unit, and a terminal carboxyl group. The novel AuNF probe (N-AuNF-Abs) was prepared by coupling the amino group of anti-ZEN antibodies with the AuNF carboxyl group via an amido covalent linkage. For comparison, a traditional AuNF probe (Tr-AuNF-Abs) was prepared by labeling antibodies on the surface of citrate capped AuNFs via an electrostatic adsorption method. The detection performance of the two probes in LFA was systematically investigated, including the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50), robustness and reproducibility for ZEN quantitative detection in DDGS samples, and shelf life. The N-AuNF-Ab based LFA (N-LFA) had a lower IC50 value (15.97 ng mL−1) for ZEN detection in phosphate buffered saline than that of the Tr-AuNF-mAb based LFA (Tr-LFA, 31.06 ng mL−1). The IC50 value of N-LFA in DDGS extract was 17.46 ng mL−1, whereas the Tr-LFA showed poor robustness and reproducibility in DDGS samples, resulting in a failed determination. The intra- and inter-assays of N-LFA for ZEN-spiked DDGS samples indicated that the average recoveries ranged from 93.0% to 125.9%, with coefficients of variation ranging from 2.8% to 21.9%. These results indicated that the N-LFA strip exhibits good robustness and an acceptable accuracy for ZEN quantitative detection in complex DDGS samples. In accelerated aging studies, N-LFA showed a longer shelf life (5 years) than that of Tr-LFA (1 year). In summary, the proposed method provided a novel strategy to prepare a super-stable probe for enhancing the detection performance of LFA for small molecular detection in complex sample matrices such as DDGS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...