Asymmetric faradaic assembly of Bi2O3 and MnO2 for a high-performance hybrid electrochemical energy storage device†
Abstract
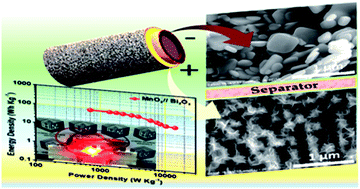
In the current study, we have explored the coupling of Bi2O3 negative electrode and MnO2 positive electrode materials as an asymmetric faradaic assembly for a high-performance hybrid electrochemical energy storage device (HEESD). Aiming at a low-cost device, both the electrodes have been synthesized by a simple, scalable, and cost-effective chemical synthesis method. After their requisite structure-morphological confirmation and correlation, these electrodes were separately examined for their electrochemical performance in a three-electrode configuration. The results obtained confirm that Bi2O3 and MnO2 exhibit 910 C g−1 and 424 C g−1 specific capacity, respectively, at 2 A g−1 current density. Notably, the performance of both electrodes has been analyzed using Dunn's method to highlight the distinct nature of their faradaic properties. Afterwards, the asymmetric faradaic assembly of both electrodes, when assembled as a HEESD (MnO2//Bi2O3), delivered 411 C g−1 specific capacity at 1 A g−1 current density due to the inclusive contribution from the capacitive as well as the non-capacitive faradaic quotient. Consequently, the assembly offers an excellent energy density of 79 W h kg−1 at a power density of 702 W kg−1, with a magnificent retention of energy density up to 21.1 W h kg−1 at 14 339 W kg−1 power density. Moreover, it demonstrates long-term cycling stability at 10 A g−1, retaining 85.2% of its initial energy density after 5000 cycles, which is significant in comparison with the previously reported literature. Additionally, to check the performance of the device in real time, two HEESDs were connected in series to power a light-emitting diode. The results obtained provide significant insight into hybrid coupling, where two different faradaic electrodes can be combined in a synergistic combination for a high-performance HEESD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...