Neuroprotective effects of myristargenol A against glutamate-induced apoptotic HT22 cell death
Abstract
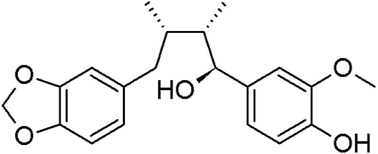
Glutamate is an important neurotransmitter in the central nervous system; however, at high concentrations, it causes excitotoxicity and many neurological disorders. Excitotoxicity induces cell death by apoptosis. Thus, factors that can inhibit the apoptotic pathways are a target of drug development for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases. Herein, the antioxidative and neuroprotective effects of myristargenol A were examined in glutamate-induced mouse hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells. When the HT22 cells were stressed with glutamate, cell viability decreased to 44.4 ± 5.6% when compared with the case of the control cells (100 ± 4.8%); however, when these cells were treated with myristargenol A (10 μM), the cell viability was increased by 113.6 ± 2.3%. The protective effect of myristargenol A against the apoptosis of glutamate-induced HT22 cells was also confirmed using FITC-annexin V/propidium iodide double staining. In addition, myristargenol A protected the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm). Subsequently, the expression levels of proteins in the caspase pathway related with the induction of apoptosis were decreased. Moreover, the expression levels of mitochondrial-related proteins, such as Bcl-2 and Bax, were examined, and it was found that the expression ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 decreased. In addition, myristargenol A inhibited the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinases, including p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase, for an oxidative stress protection effect but increased the activity of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 for cell proliferation. These results reveal that myristargenol A possesses a neuroprotective effect against the neuronal cell damage caused by glutamate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...