Comparison of the structure and function of a chimeric peptide modified titanium surface†
Abstract
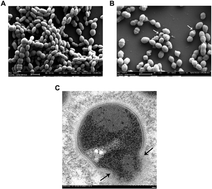
Peri-implantitis is a plaque-initiating infectious disease that can be prevented by interfering with the initial bacterial attachment. At present, surface modification of implants using antimicrobial peptides can interfere with the adhesion of streptococci. In this study, the structure and function of chimeric peptides were compared to get a strategy to modify a Ti surface. Compared to the antimicrobial activity with a fragment of hBD-3, the bifunctional and multifunctional chimeric peptides retain their antimicrobial function. All peptides showed antimicrobial activity against streptococcus in biofilm and planktonic conditions. The results demonstrate significant improvement in reducing bacterial colonization onto titanium surfaces. According to the results of structure analysis, the antimicrobial activity of tyrosine in hBD3-3 was stronger than that of the alpha helix in bifunctional or multifunctional chimeric peptides. Rigid connections were proved to avoid functional domain changes due to the interaction of charges. These results indicated that the endogenous peptide fragments modifying the Ti surface could provide an environmentally friendly approach to reduce or prevent the occurrence of peri-implant diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...