Cation exchange synthesis of CuInxGa1−xSe2 nanowires and their implementation in photovoltaic devices†
Abstract
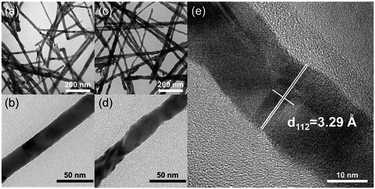
CuInxGa1−xSe2 (CIGS) nanowires were synthesized for the first time through an in situ cation exchange reaction by using CuInSe2 (CIS) nanowires as a template material and Ga-OLA complexes as the Ga source. These CIGS nanowires maintain nearly the same morphology as CIS nanowires, and the Ga/In ratio can be controlled through adjusting the concentration of Ga-OLA complexes. The characteristics of adjustable band gap and highly effective light-absorbances have been achieved for these CIGS nanowires. The light-absorbing layer in photovoltaic devices (PVs) can be assembled by employing CIGS nanowires as a solar-energy material for enhancing the photovoltaic response. The highest power conversion efficiency of solar thin film semiconductors is more than 20%, achieved by the Cu(InxGa1−x)Se2 (CIGS) thin-film solar cells. Therefore, these CIGS nanowires have a great potential to be utilized as light absorber materials for high efficiency single nanowire solar cells and to generate bulk heterojunction devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...