Novel vinyl-modified RGD conjugated silica nanoparticles based on photo click chemistry for in vivo prostate cancer targeted fluorescence imaging†
Abstract
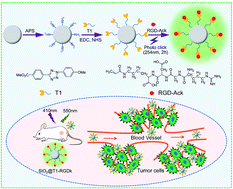
Molecular imaging is a powerful tool for non-invasive visualization of tumors that plays an important role in their diagnosis and treatment. The specificity of molecular imaging probes for cancer cells is important for accurate tumor visualization, with antibody and polypeptide nanoprobe conjugates having often been used as targeting agents for tumor detection. However, many traditional chemical conjugation methods employ complex conjugation reactions that result in poor efficiency and poor bioactivity. Herein, we describe the use of photo click methodology for the rapid synthesis of nanoprobes comprised of silica nanoparticles functionalized with RGD targeting units (SiO2@T1-RGDk NPs) (∼80 nm) for in vivo prostate cancer fluorescent imaging applications. These SiO2@T1-RGDk NPs exhibit a maximum absorption wavelength of 380 nm in their UV absorption spectra with a maximum fluorescence emission wavelength of 550 nm. Confocal immunofluorescent imaging reveal that SiO2@T1-RGDk NPs exhibit excellent targeting ability for visualizing cancer cells, with in vivo fluorescence imaging intensity in a subcutaneous tumor model of prostate cancer reaching a maxima after 4 h. Biosafety assessments showed that SiO2@T1-RGDk NPs demonstrate no obvious toxicity in mice, thus demonstrated that these novel NPs may prove to be promising fluorescent imaging agents for the accurate detection and treatment of tumors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...