Synthesis and luminescence properties of novel Eu2+/3+, Ce3+ ion single- and co-doped BaZn2(PO4)2 phosphors for white-light applications
Abstract
A series of novel Eu2+/3+, Ce3+ ion single- and co-doped BaZn2(PO4)2 samples were prepared via a high-temperature solid-state reaction. XRD powder diffraction results indicated that all of the products were pure phases. The photoluminescence properties of BaZn2(PO4)2:Eu showed that Eu2+ and Eu3+ coexist in the system and Eu3+ can be self-reduced to Eu2+ in an air atmosphere. In addition, the strongest emission peak of Eu3+ ions at 593 nm implied that Eu3+ ions occupy the inversion symmetry lattice and also the site of Zn in BaZn2(PO4). We used the theoretical method of bond energy to explain why the self-reduction of Eu3+ to Eu2+ can occur in the BaZn2(PO4)2 system. The calculation results indicated that the bond energy change value 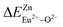 is smaller than
is smaller than 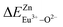 , indicating that Eu2+ ions are more likely to occupy the Zn site and more stable than Eu3+ ions in BaZn2(PO4). Furthermore, the energy transfer process between Ce3+ and Eu2+ ions in the photoluminescence spectrum and the decay lifetime were observed, and the energy transfer mechanism was determined to be a dipole–dipole interaction. In this work, by adjusting the ratio of Ce and Eu ions, the emission color can be changed from blue to white, implying that the phosphor can be used as a promising candidate in the manufacture of white LEDs.
, indicating that Eu2+ ions are more likely to occupy the Zn site and more stable than Eu3+ ions in BaZn2(PO4). Furthermore, the energy transfer process between Ce3+ and Eu2+ ions in the photoluminescence spectrum and the decay lifetime were observed, and the energy transfer mechanism was determined to be a dipole–dipole interaction. In this work, by adjusting the ratio of Ce and Eu ions, the emission color can be changed from blue to white, implying that the phosphor can be used as a promising candidate in the manufacture of white LEDs.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...