Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using endophytic bacteria and their role in inhibition of rice pathogenic bacteria and plant growth promotion
Abstract
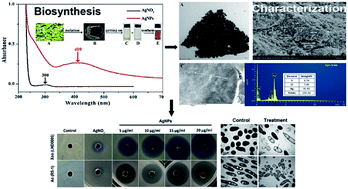
The biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) through the use of endophytic bacteria is a safe replacement for the chemical method. The study aimed to synthesize AgNPs using endophytic bacterium Bacillus siamensis strain C1, which was isolated from the medicinal plant Coriandrum sativum. The synthesized AgNPs with the size of 25 to 50 nm were further confirmed and characterized by UV-visible spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy with EDS profile. The synthesized AgNPs at 20 μg mL−1 showed a strong antibacterial effect against the pathogen of rice bacterial leaf blight and bacterial brown stripe, while an inhibition zone of 17.3 and 16.0 mm was observed for Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) strain LND0005 and Acidovorax oryzae (Ao) strain RS-1, respectively. Furthermore, the synthesized AgNPs significantly inhibited bacterial growth, biofilm formation and swimming motility of Xoo strain LND0005 and Ao strain RS-1. In addition, the synthesized AgNPs significantly increased root length, shoot length, fresh weight and dry weight of rice seedlings compared to the control. Overall, this study suggests that AgNPs have the potential to protect rice plants from bacterial infection and plant growth promotion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...