Covalently linked benzimidazole-containing reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline nanocomposites as electrode materials†
Abstract
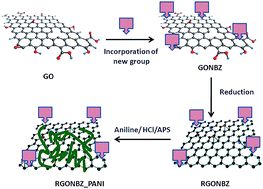
In the present manuscript, we reported the effective synthesis of 1,3-bis(2′-benzimidazolyl)-5-aminobenzene-grafted graphene oxide, followed by reduction, affording covalently linked benzimidazole-containing chemically modified reduced graphene oxide. The prepared material was further coated with polyaniline via in situ polymerization. The prepared material was successfully characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA); subsequently, it was subjected to electrochemical analysis using a three-electrode system in dilute acid solutions as electrolytes in terms of cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge–discharge and electrochemical impedance studies. The polyaniline-coated binary composite materials revealed maximum specific capacitance of 823 F g−1 at 0.2 A g−1 current density, whereas the value for the chemically modified reduced graphene oxide was 477 F g−1. The CV curves denoted the pseudocapacitive nature of the electrode materials. The values for the retention of specific capacitance for the electrode materials were 77.5% and 87.9% up to 5000 charge–discharge cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...