Polyphenols of Chinese skullcap roots: from chemical profiles to anticancer effects
Abstract
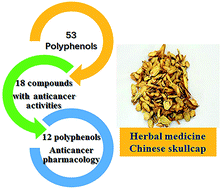
Great efforts have been made to identify the principle bioactive constituents of Chinese herbs and to unravel the molecular mechanisms behind their anticancer effects. Scutellaria baicalensis (Huangqin or Chinese skullcap) is a widely consumed herbal medicine and has been historically used in anticancer therapy in China and other countries. Chinese skullcap generates many active chemicals in the root and is abundant in polyphenols, which act as its anti-cancer ingredients. It contains around 53 polyphenols in total: 50 flavonoids and 3 stilbenes. The polyphenols have similar chemical structures since they are derived from similar biochemical synthetic pathways. According to the literature, as the active chemicals of the skullcap root, 18 polyphenols exhibit evident anticancer activities. They can be developed not only as novel candidates and precursors in anticancer drug screening, but also as important tools and agents in cancer pharmacology. We comprehensively elaborated the anticancer pharmacological properties of crude polyphenolic extracts and 12 other single compounds excluding the six well-known polyphenols, i.e., baicalein, baicalin, wogonin, wogonoside, chrysin and verbascoside. In this review, we also discussed the possible mechanisms of the anticancer effect of several skullcap polyphenols. Overall, this paper provides a unique path to understand the anticancer properties of Chinese skullcap as well as guidance to find novel anticancer drugs from a natural polyphenolic reservoir.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...