Anionic nanoparticle-lipid membrane interactions: the protonation of anionic ligands at the membrane surface reduces membrane disruption†
Abstract
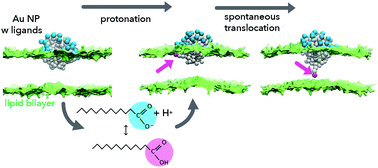
Monolayer-protected gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) are promising biomedical tools with applications in diagnosis and therapy, thanks to their biocompatibility and versatility. Here we show how the NP surface functionalization can drive the mechanism of interaction with lipid membranes. In particular, we show that the spontaneous protonation of anionic carboxylic groups on the NP surface can make the NP-membrane interaction faster and less disruptive.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...