Enhanced optical, magnetic and hydrogen evolution reaction properties of Mo1−xNixS2 nanoflakes†
Abstract
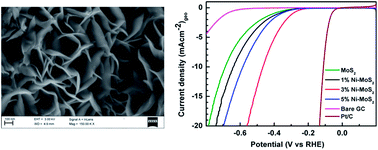
Due to exceptional electronic, optoelectronic and catalytic properties, MoS2 has attracted extensive research interest in various applications. In the present scenario, the exploitation of noble-metal-free catalysts for hydrogen evolution is of great interest. Herein, we report the structural, optical, magnetic and electrocatalytic properties of pure and nickel-substituted MoS2 nanostructures synthesized by the hydrothermal method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis reveals that all samples exhibit the hexagonal structure of MoS2 and the formation of NiS2 at higher concentrations of nickel. Vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) measurements of the Mo1−xNixS2 nanostructures show a hysteresis loop at room temperature with a higher saturation magnetization for 1% Ni-substituted MoS2 nanostructures, confirming the ferromagnetic behaviour of the sample. The indirect-to-direct band gap transition of few-layered nanostructures was confirmed by the optical absorption spectrum showing bands in the 600–700 nm and 350–450 nm regions. This study also highlights the excitation wavelength-dependent down- and up-conversion photoluminescence of the as-synthesized samples, providing new horizons for the design of MoS2-based optical and spintronic devices. The electrocatalytic effect of 3% Ni-substituted MoS2 nanostructures has been found to be higher than that of other deposit concentrations as it corresponds to the efficient hydrogen evolution reaction (HER).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...