Synthesis and characterization of polyaniline, polypyrrole and zero-valent iron-based materials for the adsorptive and oxidative removal of bisphenol-A from aqueous solution†
Abstract
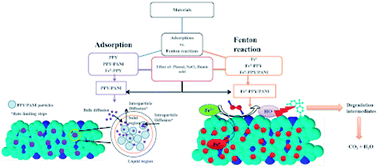
One pot synthesis of a polypyrrole, polyaniline and Fe0 nano-composite (Fe0-PPY/PANI) was achieved by polymerizing aniline and pyrrole with FeCl3 followed by the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe0 with NaBH4. PPY/PANI was synthesized the same way as Fe0-PPY/PANI, except that all the FeCl3 was removed by rinsing. The presence of Fe0 was demonstrated using several analytical techniques; this was shown in comparison to materials that are without Fe0. A series of materials were screened as both adsorbents and catalyst for the activation of H2O2 towards bisphenol A (BPA) removal in batch experiments. Polymers performed better than composites containing Fe0 at adsorption, whereas Fe0 based materials were better catalysts for the activation of H2O2. BPA samples were then spiked with other contaminants including sewage water to test the performance of the various adsorbents and Fenton catalysts. PPY/PANI was found to be a better adsorbent than the rest, whereas Fe0-PPY/PANI was the best Fenton catalyst. The adsorption kinetics of BPA onto PPY/PANI was studied; it was found that the process was governed by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The adsorption isotherms revealed that the amount of BPA taken up by PPY/PANI increased with increasing temperature and was governed by the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. The mechanism in which Fe0-PPY/PANI and H2O2 degraded BPA was studied, it was found that surface-bound hydroxyl radicals were responsible for the degradation of BPA. It was also shown that the degradation process included the formation of smaller compounds leading to the reduction of the total organic content by 57%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...