Importance of protein flexibility in ranking ERK2 Type I1/2 inhibitor affinities: a computational study†
Abstract
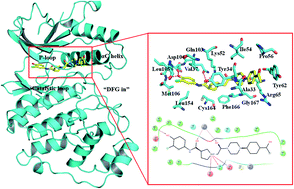
Extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK2) has been regarded as an essential target for various cancers, especially melanoma. Recently, pyrrolidine piperidine derivatives were reported as Type I1/2 inhibitors of ERK2, which occupy both the ATP binding pocket and the allosteric pocket. Due to the dynamic behavior of ERK2 upon the binding of Type I1/2 inhibitors, it is difficult to predict the binding structures and relative binding potencies of these inhibitors with ERK2 accurately. In this work, the binding mechanism of pyrrolidine piperidines was discussed by using different simulation techniques, including molecular docking, ensemble docking based on multiple receptor conformation, molecular dynamics simulations and free energy calculations. Our computational results show that the traditional docking method cannot predict the relative binding ability of the studied inhibitors with high accuracy, but incorporating ERK2 protein flexibility into docking is an effective method to improve the prediction accuracy. It is worth noting that the binding free energies predicted by MM/GBSA or MM/PBSA based on the MD simulations for the docked poses have the highest correlation with the experimental data, which highlights the importance of protein flexibility for accurately predicting the binding ability of Type I1/2 inhibitors of ERK2. In addition, the comprehensive analysis of several representative inhibitors indicates that hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions are of significance for improving the binding affinities of the inhibitors. We hope this work will provide valuable information for further design of novel and efficient Type I1/2 ERK2 inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...