RNA ligation of very small pseudo nick structures by T4 RNA ligase 2, leading to efficient production of versatile RNA rings†
Abstract
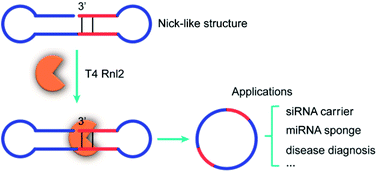
T4 RNA ligase 2 catalyses two types of reactions: (i) sealing of a nick structure in double-stranded RNA and (ii) connection of two single-stranded RNA strands. In order to obtain comprehensive views on these two types of reactions and widen the application scope of this RNA ligase, we here systematically analysed the connection of single-stranded RNA strands having different secondary structures. It has been found that the ligation is enormously promoted when a stem of only 4-bp or longer is formed in the 3′-OH side of the joining site. Additional placement of a stem in the 5′-phosphate side further facilitates the ligation. In contrast, perturbation of the stem structures in RNA substrates suppresses the ligation. These results indicate that ligation of two single-stranded RNA strands by T4 RNA ligase 2 is greatly promoted by forming a “nick-like intermediate”. Even the unstable intermediate, formed only temporarily in the solution, is sufficiently effective. By designing the synthetic systems in terms of this finding, short single-stranded RNA rings of versatile sizes, which are otherwise hard to be obtained, are efficiently prepared in high selectivity and yield.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...