Celecoxib attenuates hepatocellular proliferative capacity during hepatocarcinogenesis by modulating a PTEN/NF-κB/PRL-3 pathway†
Abstract
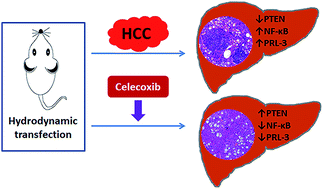
Although the efficacy of celecoxib on various cancer cell behaviors, including aberrant proliferation, in cultured hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells has been demonstrated, whether celecoxib regulates cell proliferation by targeting PRL-3-associated signaling transduction during hepatocarcinogenesis in vivo has been incompletely studied. Here, we investigate the anti-proliferative efficacy of celecoxib in a rapid HCC mouse model established by hydrodynamic transfection of activated AKT and c-Met proto-oncogenes. The results show that celecoxib is effective at delaying the malignant transformation of hepatocytes by reducing the protein expression of Ki67, Cyclin D1 and c-Myc in the AKT/c-Met HCC-bearing mice. Mechanistically, celecoxib increases the protein expression of PTEN and suppresses the protein expression of NF-κB and PRL-3 in the liver of the HCC mice. Using PTEN-silenced and LPS-stimulated approaches in vitro, a mechanism by which celecoxib regulates a PTEN/NF-κB/PRL-3 pathway in HCC cells was illuminated. Altogether, our study demonstrates that celecoxib attenuates the hepatocellular proliferative capacity during hepatocarcinogenesis, which is probably attributable to its regulation of the PTEN/NF-κB/PRL-3 pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...