A magnetically recyclable superparamagnetic silica supported Pt nanocatalyst through a multi-carboxyl linker: synthesis, characterization, and applications in alkene hydrosilylation†
Abstract
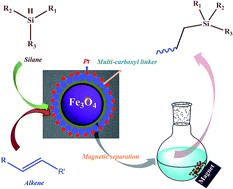
To simplify separation procedures, improve the reusability and decrease the loss of Pt, two Pt catalysts anchored on superparamagnetic silica (Fe3O4@SiO2-EDTA@Pt and Fe3O4@SiO2-DTPA@Pt) were prepared for the first time. The stable magnetic properties made them easily recyclable using a magnet rather than filtration, decantation or centrifugation. After 12 catalytic runs for both 30–50 nm Pt catalysts, the yield of 1-heptylmethyldichlorosilane was still up to 90%. The average loss of Pt in each reaction was only 0.87% for Fe3O4@SiO2-EDTA@Pt and 0.66% for Fe3O4@SiO2-DTPA@Pt owing to the strong interaction between Pt and carboxyl. The unprecedented activity and selectivity of the two Pt nanoparticle catalysts were observed in the hydrosilylation of alkenes. The turnover number in the reaction between 1-hexene and methyldichlorosilane using 5 × 10−8 mol of the Pt approached 662 733 for Fe3O4@SiO2-EDTA@Pt and 579 947 for Fe3O4@SiO2-DTPA@Pt over 12 h. The corresponding hydrosilylation products in excellent yields were obtained when we employed a broad range of alkenes as substrates, including 5 isomerous hexenes and 14 important industry raw materials. Fe3O4@SiO2-DTPA@Pt showed a better activity. They have potential for catalyzing more reactions and replacing the current homogeneous Pt catalysts in industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...