Recycling of vitrimer blends with tunable thermomechanical properties†
Abstract
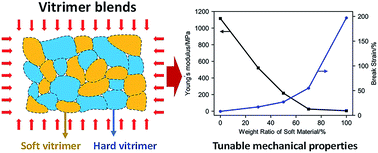
Vitrimers are a new class of thermosetting polymers that can be thermally processed through bond exchange reactions (BERs) without losing network integrity. In engineering applications, the tunability of their thermomechanical properties is highly desirable to meet the requirements of different working conditions. Here, we report a simple composite-based strategy that avoids complex chemistry to prepare vitrimer blends with tunable thermomechanical properties by virtue of the good weldability of base vitrimers. Effects of processing parameters (such as temperature and time) on the properties of recycled vitrimer blends are experimentally investigated. A computational model that accounts for the random distribution of component vitrimer particles is developed to predict the thermomechanical properties of the recycled vitrimer blends with various compositions. Good agreement is achieved between theoretical prediction and experiment. Parametric studies are further conducted by employing the computational model to explore the designability and provide some basic principles to guide the design of recycled vitrimer blends. Reasonable recyclability of the vitrimer blends is verified by multiple generations of recycling experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...