The interaction of dietary flavonoids with xanthine oxidase in vitro: molecular property-binding affinity relationship aspects
Abstract
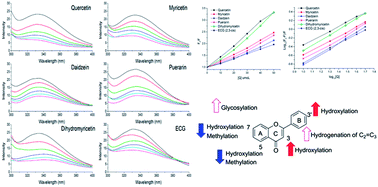
The molecular property–affinity relationships of dietary flavonoids binding to xanthine oxidase were investigated in vitro by comparing the binding constants obtained from a fluorescence-quenching method. The inhibitions of dietary flavonoids on xanthine oxidase were also investigated and analyzed, revealing that the binding process was influenced by the structural differences of the flavonoids under investigation. For example, methylation and hydroxylation at the 7- and 5-positions weakened the binding affinities, while hydroxylation at the 3- and 3′-positions mostly improved binding affinities. Glycosylation and hydrogenation of the C2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C3 double bond also increased affinities for xanthine oxidase. In addition, galloylated catechins showed higher binding affinities than non-galloylated catechins. Trends in the binding affinities and inhibition of flavonoids during structure modifications were summarized. Affinities for xanthine oxidase and inhibition on xanthine oxidase changed in the opposite direction during the methylation and hydroxylation of flavonoids in the A ring, and the glycosylation and hydrogenation of C2
C3 double bond also increased affinities for xanthine oxidase. In addition, galloylated catechins showed higher binding affinities than non-galloylated catechins. Trends in the binding affinities and inhibition of flavonoids during structure modifications were summarized. Affinities for xanthine oxidase and inhibition on xanthine oxidase changed in the opposite direction during the methylation and hydroxylation of flavonoids in the A ring, and the glycosylation and hydrogenation of C2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C3. However, affinities and inhibition for xanthine oxidase changed in the same direction during the methylation and hydroxylation of flavonoids in the B ring.
C3. However, affinities and inhibition for xanthine oxidase changed in the same direction during the methylation and hydroxylation of flavonoids in the B ring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...