Isolation of maltol derivatives from Stellera chamaejasme and the anti-atopic properties of maltol on skin lesions in DNCB-stimulated mice†
Abstract
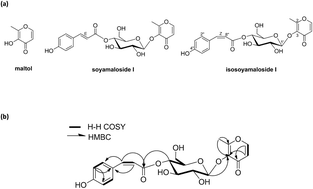
The aim of this study was to isolate maltol derivatives from S. chamaejasme and to investigate the anti-atopic dermatitis (anti-AD) effect of maltol in a 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)-sensitized mouse model of AD. A novel compound, maltol 3-O-(4′-O-cis-p-coumaroyl)-β-D-glucoside (named isosoyamaloside I), and two known maltol derivatives (maltol and soyamaloside I) were isolated from S. chamaejasme using chromatographic methods. Dermal application of maltol to DNCB-sensitized AD mice reduced erythema, pruritus, and lichenification scores. Histopathological examinations revealed significant decline in mast cell infiltration in maltol-treated AD mice. In addition, maltol accelerated skin barrier recovery by reducing TEWL and skin pH and increasing skin hydration. Maltol was also found to suppress atopy-induced IL-4 and IgE elevations in serum, which are known to be essential for the development of atopy. The results of this study show that maltol is a potential therapeutic candidate for the treatment of AD-related skin diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...