Simultaneous immobilization of NH4+ and Mn2+ from electrolytic manganese residue using phosphate and magnesium sources
Abstract
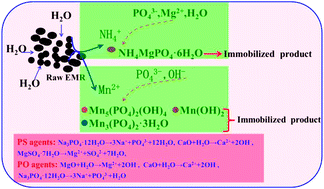
Immobilization of contaminants from electrolytic manganese residue (EMR) is essential for the safe stacking and reuse of EMR. This study provides experiment results for the simultaneous immobilization of NH4+ and Mn2+ from EMR using Na3PO4·12H2O and MgSO4·7H2O (PS) agents, as well as Na3PO4·12H2O and MgO (PO) agents. The optimum reaction conditions, characteristics of immobilization, mechanism and the economy of alternative chemicals were determined and are discussed. The results indicated that the immobilization efficiencies of NH4+ and Mn2+ were 92.4% and 99.9% respectively under the following conditions: a MgSO4·7H2O : Na3PO4·12H2O : EMR mass ratio of 0.113 : 0.175 : 1, a CaO : EMR mass ratio of 0.03 : 1 and a reaction time of 1 h using PS agents. The concentration of NH4+ in the leach liquor reduced from 1264 to 98 mg L−1 after immobilization. The concentration of heavy metal ions decreased sharply in the leach liquor and met the Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard of China (GB8978-1996). The characteristics of immobilization indicated that NH4+ was immobilized to form NH4MgPO4·6H2O and that Mn2+ was immobilized to form Mn5(PO4)2(OH)4, Mn3(PO4)2·3H2O and Mn(OH)2. An economic evaluation showed that using PS agents had lower associated cost than using PO agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...