The caffeic acid moiety plays an essential role in attenuating lipid accumulation by chlorogenic acid and its analogues†
Abstract
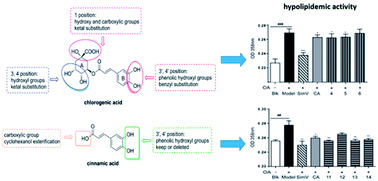
Chlorogenic acid (5-caffeoylquinic, CA) possesses distinct hypolipidemic properties in vivo and in vitro, yet the structure–activity relationship (SAR) of CA on lipid metabolism remains unknown. To achieve this aim, we designed and synthesized two sets of CA analogues and evaluated their efficacies to prevent oleic acid (OA)-elicited lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Blockage of all hydroxyl and carboxyl groups on the quinic acid moiety did not deteriorate the hypolipidemic effect of CA while blockage of all phenolic hydroxyl groups on the caffeic acid moiety abolished the activity of CA. Further replacement of the quinic acid moiety with cyclohexane and modification of individual phenolic hydroxyl groups on the caffeic acid moiety showed that the phenolic-hydroxyl-reserved analogues displayed a more potent hypolipidemic effect than CA, whereas the analogue with no phenolic hydroxyl displayed little effect on the OA-elicited lipid accumulation. In accordance, the modulating effects of CA on the transcription of the lipogenic gene sterol-regulatory element binding protein (SREBP)1c/1a, acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FAS) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) were also abolished when the phenolic hydroxyl groups on the caffeic acid moiety were blocked. Our results suggest that the phenolic hydroxyl on the caffeic acid moiety is vital for the lipid-lowering activity of CA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...