Orientation effects on the nanoscale adsorption behavior of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on hydrophilic silicon dioxide†
Abstract
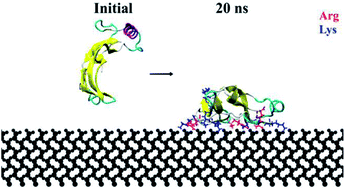
Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (BMP-2) is a growth factor associated with different developmental functions in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Because of its favorable properties for the development of bone and cartilage tissue, BMP-2 promotes the biocompatibility of medical implants. In this research, molecular dynamics simulations were implemented to simulate the interaction of BMP-2 with a flat hydrophilic silicon dioxide substrate, an important biomaterial for medical applications. We considered the influence of four orthogonal protein orientations on the adsorption behavior. Results showed that arginine and lysine were the main residues to interact with the silicon dioxide substrate, directly adsorbing onto the surface and overcoming water layers. However, between these charged residues, we observed a preference for arginine to adsorb. Orientations with the α-helix loop closer to the surface at the beginning of the simulations had greater loss of secondary structure as compared to the other configurations. Among all the orientations, the end-on B configuration had favorable adsorption characteristics with a binding energy of 14 000 kJ mol−1 and retention of 21.7% β-sheets as confirmed by the Ramachandran plots. This research provides new insights into the nanoscale interaction of BMP-2 and silicon dioxide substrate with applications in orthopedic implants and regenerative medicine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...