Intracellular processing of silica-coated superparamagnetic iron nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells†
Abstract
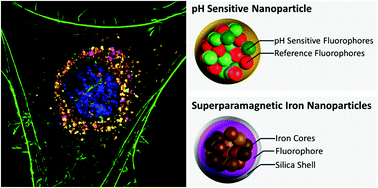
Silica-coated superparamagnetic iron nanoparticles (SiMAGs) are an exciting biomedical technology capable of targeted delivery of cell-based therapeutics and disease diagnosis. However, in order to realise their full clinical potential, their intracellular fate must be determined. The analytical techniques of super-resolution fluorescence microscopy, particle counting flow cytometry and pH-sensitive nanosensors were applied to elucidate mechanisms of intracellular SiMAG processing in human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSCs). Super-resolution microscopy showed SiMAG fluorescently-tagged nanoparticles are endocytosed and co-localised within lysosomes. When exposed to simulated lysosomal conditions SiMAGs were solubilised and exhibited diminishing fluorescence emission over 7 days. The in vitro intracellular metabolism of SiMAGs was monitored in hMSCs using flow cytometry and co-localised pH-sensitive nanosensors. A decrease in SiMAG fluorescence emission, which corresponded to a decrease in lysosomal pH was observed, mirroring ex vivo observations, suggesting SiMAG lysosomal exposure degrades fluorescent silica-coatings and iron cores. These findings indicate although there is a significant decrease in intracellular SiMAG loading, sufficient particles remain internalised (>50%) to render SiMAG treated cells amenable to long-term magnetic cell manipulation. Our analytical approach provides important insights into the understanding of the intracellular fate of SiMAG processing, which could be readily applied to other particle therapeutics, to advance their clinical translation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...