Electrochemical estimation of active site density on a metal-free carbon-based catalyst†
Abstract
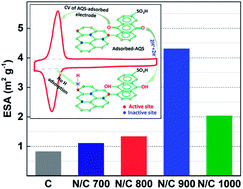
Nitrogen-doped carbon is synthesized by the heat-treatment of carbon in an ammoniacal atmosphere at different temperatures. The active site density and electrochemically active surface area (ESA) of carbon and nitrogen-doped carbon catalysts are estimated from the charge due to oxidation of the adsorbed anthraquinone-2-sulfonate (AQS) probe molecule. In the potential window of interest and over a range of concentrations, there is no unwanted side reaction or polymerization of the probe molecule that interferes with the electrochemical estimation of active site density. Most importantly, the adsorbed AQS can easily be removed from the electrode surface by potential cycling. The ORR activity and active site density of the catalysts derived from AQS-adsorption have similar trends. The active site density and turnover frequency towards ORR estimated using the AQS-adsorption method are in line with those reported in the literature by other methods. On the other hand, the results show that the wetted surface area estimated from the double layer capacitance does not always correlate with catalytic activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...