Preventive effect of oligonol on nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species production through regulation of nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells against sodium nitroprusside
Abstract
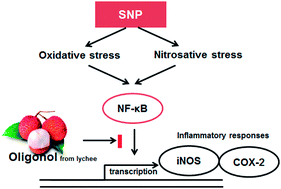
Oligonol, a low-molecular weight polyphenol isolated from lychee fruit, has been shown to possess beneficial properties, including anti-oxidative, anti-diabetic, and hepatoprotective properties in vitro and in vivo. This study was performed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of oligonol using sodium nitroprusside (SNP)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Our results demonstrated that exposure of SNP to RAW 264.7 cells significantly decreased cell viability, and increased nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. However, treatment with oligonol inhibited cell death and suppressed the over-production of NO and ROS induced by SNP in a dose-dependent manner. Consistent with these findings, oligonol significantly downregulated the mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory mediators, inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2, when compared with the SNP-treated control group. Furthermore, suppression of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation was also observed after treatment with oligonol in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. These results suggest that oligonol attenuated SNP-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses via regulation of the NF-κB signalling pathway. On the basis of such potent anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, we propose that oligonol may contribute in the prevention and treatment of inflammation-related disorders.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...