High-throughput metabolic profiling, combined with chemometrics and bioinformatic analysis reveals functional alterations in myocardial dysfunction†
Abstract
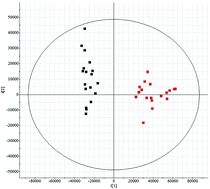
High-throughput metabolic profiling technology has been used for biomarker discovery and to reveal underlying metabolic mechanisms. Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SMD) is a common complication in sepsis patients, and severely affects their quality of life. However, the pathogenesis of SMD is currently unclear, and there has been inadequate basic research. In this study, metabolic profiling was explored by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) combined with chemometrics and bioinformatic analysis. The global metabolome data were analyzed using chemometrics analysis including principal component analysis and partial least squares discriminant analysis for significant metabolites. Variable importance for projection values obtained utilizing a pattern recognition method were used to identify potential biomarkers. The differential metabolites were putatively identified using the metabolome database and bioinformatics analysis was conducted via Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) to predict the likely functional alterations. In total, 21 differential metabolites were found in SMD and these were involved in phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis, arachidonic acid metabolism, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, and so on. The analysis revealed that the metabolites were strongly related to molecular transport, and small molecule biochemistry metabolic pathways. The present study indicates that high-throughput metabolic profiling, combined with chemometrics and a bioinformatic platform, can reveal the likely functional alterations in disease and could provide more precise and credible information in the basic research of disease pathogenesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...