More than a CO source: palladium-catalyzed carbonylative synthesis of butenolides from propargyl alcohols and TFBen†
Abstract
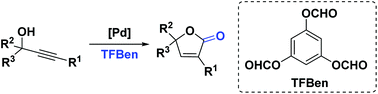
Palladium-catalyzed direct carbonylation of propargyl alcohols for the synthesis of butenolides has been achieved. This transformation employs benzene-1,3,5-triyl triformate (TFBen) as the CO source and provides a facile and straightforward access to various substituted butenolides in high yields (up to 85%). Notably, phloroglucinol as the decomposed product of TFBen promotes the formation of butenolides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...