Naphthomycin-derived macrolactams with two new carbon skeletons from endophytic Streptomyces†
Abstract
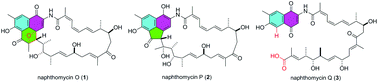
Chemical investigation of an endophytic Streptomyces strain led to the isolation of naphthomycin congeners 1–4. Compound 1 contains a unique phenalene scaffold with a bridged oxetane ring, which was confirmed to be a result of an intramolecular [2 + 2] cycloaddition between the olefin and the ketone in the known compound 4 by chemical conversion. 2 features an unprecedented acenaphthene moiety in the ansamycin class of polyketides. Possible biosynthetic pathways are proposed for 1–3. Compounds 1–3 were tested for cytotoxicity against selected human cancer cell lines and they showed moderate activity, with IC50 values ranging from 10.6 μM to 32.5 μM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...