LaZrCeO/YSZ TBCs by EB-PVD: microstructural evolution, residual stress and degradation behavior
Abstract
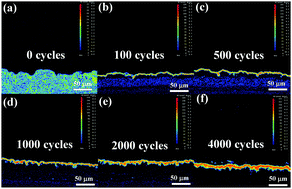
The present study focuses on microstructural evolution, element diffusion and degradation behavior in LaZrCeO/yttria-stabilized zirconia (LZC/YSZ) thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) at 1300 °C. The NiCoCrAlYHf and LZC/YSZ coatings are prepared by arc ion-plating PVD and electron beam-physical vapor deposition. Characterization methods include scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and field emission-electron probe micro-analysis. The results reveal that the LZC/YSZ coating shows a relatively high thermal shock lifetime at 1300 °C. The TGO thickens and grows corresponding to parabolic growth kinetics along with the thermal shock process. The value of compressive stress reaches the highest value of 2.56 GPa at 1000 thermal shock cycles. The LZC/YSZ coating shows a relatively high thermal stability at 1300 °C. Obvious element diffusion takes place in the DCL TBCs, leading to the formation of Hf–Y–Al oxides and Ni–Co–Cr oxides in the thermally grown oxide (TGO) layer at 1300 °C. In particular, La2Zr2O7 might react with Cr and O2 once the Cr element diffuses to the LZC coating from the bond coat. The evolution of the TGO microstructure, cracks, residual stress and element depletion appear to be relevant to the durability and degradation of TBCs. This work will provide some valuable insight for understanding the failure of TBCs under higher service temperatures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...