Si nanoparticles embedded in 3D carbon framework constructed by sulfur-doped carbon fibers and graphene for anode in lithium-ion battery
Abstract
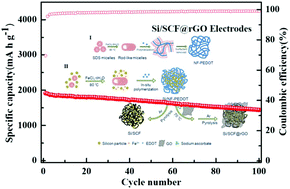
One of the key technical challenges in the practical application of high-capacity Si-based anode materials in lithium-ion batteries is to enhance the cycling stability of the electrode. In this report, Si nanoparticles incorporated with a 3D carbon hybrid framework composed of S-doped carbon fibers and reduced graphene oxide (Si/SCF@rGO) was synthesized by combining the in situ polymerization of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) with chemical reduction and the pyrolysis process. The Si nanoparticles were well dispersed in the 3D carbon hybrid framework, which was further confirmed by SEM, TEM, and XRD. Owing to its well-constructed structure, which is favorable for fast charge transfer, the Si/SCF@rGO composite was tested as an anode in a lithium-ion battery. When cycled at 400 mA g−1, a reversible capacity of 1441.0 mA h g−1 could be retained after 100 cycles. Even when the current density increased to 3.2 A g−1, the reversible capacity could reach 572.1 mA h g−1. The enhanced cycling performance can be ascribed to the hierarchical structure of the carbon framework. The SCF in the carbon hybrid framework improves the dispersion and enhances the electron transfer between the Si nanoparticles. Also, the void surrounding the Si nanoparticles constructed by rGO could effectively accommodate the volume expansion and provide an extra protective layer for the active material to prevent the direct contact with the electrolyte, thus contributing to a comparably stable electrode structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...