Incorporation of bifunctional aminopyridine into an NbO-type MOF for the markedly enhanced adsorption of CO2 and C2H2 over CH4†
Abstract
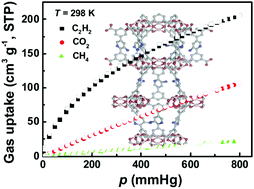
The development of porous MOFs exhibiting highly selective C2H2/CH4 and CO2/CH4 separations is quite important to meet the requirement of high-purity C2H2 and CH4 in various industries. By employing a ligand heterobifunctionalization strategy, we designed and synthesized an aminopyridine-functionalized diisophthalate ligand, and successfully targeted its corresponding copper-based NbO-type MOF ZJNU-98. Gas adsorption studies revealed that ZJNU-98 exhibited significantly enhanced adsorption of C2H2 and CO2 over CH4 compared to its parent MOF, NOTT-101. At 298 K and 1 atm, C2H2 and CO2 uptakes of ZJNU-98 are 10.0% and 16.7% higher than the corresponding values of NOTT-101, while 14.2% and 18.8% increases in C2H2/CH4 and CO2/CH4 adsorption selectivities were observed for the equimolar gas mixtures in ZJNU-98 compared to NOTT-101. Furthermore, the contribution of the functional group effect on gas adsorption has been assessed, demonstrating that the amine group plays a more important role than the pyridinic-N atom despite its lower Lewis basicity. This work provided an effective way and significant experimental evidence for the design of new porous MOFs with highly enhanced gas adsorption performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...