Cost-effective preparation of microporous polymers from formamide derivatives and adsorption of CO2 under dry and humid conditions†
Abstract
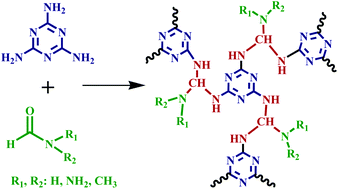
Nitrogen-rich microporous polymers that contain different contents of primary, secondary and tertiary amine groups in their networks are prepared via the amine-formamido condensation reaction utilizing formamide, formohydrazide, N-methylformamide and N,N-dimethylformamide as starting monomers to polymerize with melamine, respectively, via a facile one-step polymerization reaction in the absence of any catalyst. The resultant four polymers exhibit BET surface areas of 612–748 m2 g−1 and adjustable pores sizes in the range from 0.52 to 1.10 nm. The systematically changed types of amine groups and porosity parameters result in interesting variations of interfacial interactions between the porous surface and CO2 molecule, so as to significantly influence the adsorption behaviour of CO2 gas. The uptake of CO2 in polymers is up to 14.6 wt% (273 K/1.0 bar) with an outstandingly high CO2/N2 adsorption selectivity of 151. Moreover, after adding a small amount of water vapour in the mixed CO2/N2 gas, the adsorption selectivity CO2/N2 further increases to 173. The adsorption of CO2 and its selectivity over N2 in this series of microporous polymers under both dry and humid conditions are studied and discussed in terms of the type of the amine group on the polymer skeletons, the adsorption mechanism and the porosity parameters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...