Tumor-targeting intracellular drug delivery based on dual acid/reduction-degradable nanoassemblies with ketal interface and disulfide core locations†
Abstract
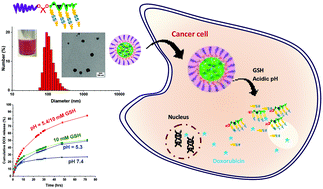
Smart nanoassemblies based on well-controlled block copolymers degradable in response to dual endogenous stimuli, particularly acidic pH and glutathione (reduction) found in tumor tissues and cancer cells, are promising candidates as tumor-targeting drug delivery nanocarriers. Here, we report an approach to develop dual acid/reduction-degradable block copolymer nanoassemblies having acid-cleavable ketal linkages at core/corona interfaces and disulfide pendants in micellar cores, thus attaining dual stimuli responses at dual locations. The approach employing reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization with a newly synthesized poly(ethylene glycol)-based macro-RAFT agent labeled with a ketal linkage (PEG-ketal-RAFT, P4) allows for the synthesis of a well-controlled block copolymer (P5) composed of a hydrophilic PEG block connected through a ketal linkage with a hydrophobic methacrylate block having pendant disulfide linkages. The amphiphilic nature of P5 ensures the fabrication of nanoassemblies loaded with doxorubicin (a clinically used anticancer drug) through aqueous micellization. Not only the cleavage of the ketal linkages in endosomal or lysosomal pH sheds coronas at interfaces, but also the reductive cleavage of pendant disulfides to the corresponding thiols in the presence of cellular glutathione causes a change in the hydrophobic/hydrophilic balance in micelle cores. These dual acid/reduction responses that occurred at dual locations lead to the synergistic and accelerated drug release, compared with single response at single location. These results, combined with in vitro cell culture experiments including cell viability and cellular uptake, demonstrate the versatility of dual location dual acidic pH/reduction-responsive degradation in the development of tumor-targeting intracellular drug delivery vehicles for cancer chemotherapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...