Thermoset elastomers covalently crosslinked by hard nanodomains of triblock copolymers derived from carvomenthide and lactide: tunable strength and hydrolytic degradability†
Abstract
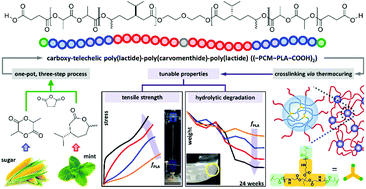
A hydrolytically degradable and mechanically reinforced thermoset elastomer system using plant-derived monomers was developed via three synthetic steps in one pot and a subsequent thermal curing process. First, through consecutive controlled ring-opening polymerization reactions, hydroxyl-terminated poly(carvomenthide) (–PCM–OH)2 homopolymers with desirable elastomeric properties were precisely prepared with target values of 10, 12, 14, and 16 kg mol−1 and were subsequently block-copolymerized with D,L-lactide (LA) for mechanical enhancement and degradability to synthesize hydroxyl-terminated poly(lactide)–poly(carvomenthide)–poly(lactide) (–PCM–PLA–OH)2 triblocks (total Mn = ∼20 kg mol−1). Second, the resulting triblock diols were functionalized by post-polymerization esterification using an organic acid anhydride to give thermoplastic carboxy-telechelic (–PCM–PLA–COOH)2 polyesters as thermoset precursors, having fPLA values of 0.20, 0.30, 0.40, and 0.45. Finally, the thermoset processing of the PLA hard domains was performed with multifunctional aziridine to yield crosslinked XL–(PLA–PCM–PLA) elastomers having gel fractions above 95%. The high thermal stability, well-defined microphase-separated morphology, superior and tunable mechanical strength, and controlled hydrolytic degradability were systematically investigated, when compared to those of the triblock prepolymers. The hard domain crosslinked thermoset elastomers with tunable mechanical strength and degradation capability can be practical candidates for sustainable elastomers to satisfy distinct and high-performance applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...