Functional cationic derivatives of starch as antimicrobial agents†
Abstract
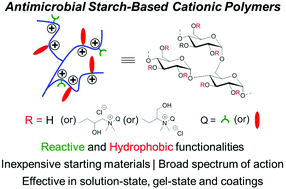
Antimicrobial polymers with a broad spectrum of action and high selectivity towards pathogens (versus mammalian cells) provide the opportunity to combat infections with only a limited chance of resistance development. To this end, functional antimicrobial biodegradable materials derived from inexpensive renewable resources such as polysaccharides would pave the way for broader applications. Here we report a facile one-pot approach to access potent functional antimicrobial polymers from soluble starch, a renewable plant-based starting material and other readily available reagents. In solution-state, these polymers with optimal composition demonstrate excellent antibacterial activity, but limited antifungal properties. The reactive allyl groups installed onto this polymeric platform enabled seamless translation of these polymers into antimicrobial hydrogels and coatings via photo-mediated thiol–ene reactions. Both the hydrogels and hydrogel-coated cotton-pads exhibited high killing efficiencies across multiple strains of pathogens (∼100% for S. aureus, E. coli and P. aeruginosa). Installation of reactive groups onto antimicrobial platforms allows for rapid development of formulations and prototypes in different forms such as solutions, gels and surface coatings by minimizing or completely eliminating the need to optimize the polymer to suit different applications. These results demonstrate the potential utility of cationic starch-based biodegradable polymers as antimicrobial materials and coatings for the prevention of infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...